Delve into the realm of health insurance plans and discover the diverse options available for your coverage needs. This comprehensive guide offers insights into the nuances of each plan type, helping you navigate the complex landscape of healthcare insurance with confidence.
Explore the intricacies of HMOs, PPOs, EPOs, and POS plans, uncovering the key differentiators that set them apart and learning how to leverage each plan to your advantage.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance is a type of coverage that helps pay for medical and surgical expenses incurred by the insured. It provides financial protection against costly healthcare services.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
- HMO plans require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain referrals to see specialists.
- These plans typically have lower out-of-pocket costs, but less flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
- They are suitable for individuals who prefer lower premiums and are willing to coordinate care through a primary physician.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
- PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and do not require referrals to see specialists.
- Members can see out-of-network providers, but at a higher cost.
- These plans are beneficial for individuals who want a balance between cost and provider choice.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
- EPO plans only cover services provided by in-network healthcare providers, except in emergencies.
- Members do not need referrals to see specialists and typically have lower premiums.
- They are suitable for individuals who want cost-effective coverage and are willing to stay within a network for care.
Point of Service (POS)
- POS plans combine features of HMO and PPO plans, offering lower costs for in-network care and the option to see out-of-network providers.
- Members need referrals to see specialists, but have more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
- These plans are beneficial for individuals who want cost savings but also desire some out-of-network coverage.
Healthcare Access
Access to healthcare refers to an individual’s ability to obtain timely and appropriate medical services when needed. It is a critical aspect of overall health and well-being, as it directly impacts the quality of care received and health outcomes. Ensuring healthcare access for all individuals is essential for promoting a healthy population and preventing unnecessary suffering and complications.
Impact of Different Health Insurance Plans on Healthcare Access
Health insurance plans play a significant role in determining an individual’s access to healthcare services. Different types of insurance plans can have varying impacts on healthcare access based on factors such as cost, coverage, provider networks, and restrictions.
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Plans: HMOs typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain referrals for specialist care. While these plans often have lower out-of-pocket costs, they can limit access to out-of-network providers and require strict adherence to network guidelines.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) Plans: PPOs offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and do not require referrals for specialist care. While they tend to have higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs, they provide broader access to a larger network of providers.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) Plans: EPOs combine elements of HMOs and PPOs by offering coverage within a specific network of providers. They do not require referrals for specialist care but have limited coverage for out-of-network services, which can impact access to certain providers.
- Point of Service (POS) Plans: POS plans allow members to choose between in-network and out-of-network providers. While they require referrals for specialist care, they offer greater flexibility in provider selection but may come with higher out-of-pocket costs.
Strategies for Maximizing Healthcare Access with Different Insurance Plans
- Understand Your Plan: Familiarize yourself with the details of your health insurance plan, including coverage, network providers, and any restrictions or requirements.
- Choose Providers Wisely: Select healthcare providers within your plan’s network to minimize out-of-pocket costs and ensure coverage for services.
- Utilize Preventive Services: Take advantage of preventive care services covered by your plan to maintain good health and potentially avoid more serious health issues.
- Appeal Denials: If a claim is denied by your insurance company, you have the right to appeal the decision and advocate for coverage of necessary healthcare services.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with changes in your plan’s coverage and network providers to make informed decisions about your healthcare needs.
Healthcare Costs
The costs associated with healthcare can vary greatly depending on several factors, including the type of treatment needed, the provider, and the location. These costs can quickly add up, making it essential to have a health insurance plan in place to help manage expenses.
Factors Influencing Healthcare Costs
- Medical procedures required
- Specialized treatments
- Healthcare provider fees
- Geographic location
Health Insurance Plans and Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Health insurance plans play a crucial role in reducing out-of-pocket expenses for individuals. By covering a portion of medical costs, insurance plans help alleviate the financial burden on policyholders. However, the extent of coverage and out-of-pocket expenses can vary depending on the type of insurance plan.
Cost-Sharing Mechanisms in Insurance Plans
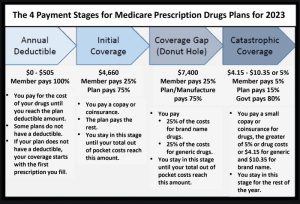
- Deductibles: Amount individuals pay before insurance coverage kicks in.
- Co-payments: Fixed amount paid for each healthcare service or prescription.
- Co-insurance: Percentage of costs shared between the individual and the insurance company.
Strategies for Managing Healthcare Costs
- Choose an insurance plan with lower deductibles if you anticipate frequent medical visits.
- Utilize in-network providers to take advantage of negotiated rates.
- Consider a Health Savings Account (HSA) to save for future medical expenses tax-free.
Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in the context of health insurance by delivering medical services to individuals covered by insurance plans. These providers can include doctors, specialists, hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities.
Role of Different Insurance Plans
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plans typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain referrals to see specialists within the network.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, both in and out of network, but at a higher cost.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) plans limit coverage to healthcare providers within the designated network, except in emergencies.
- Point of Service (POS) plans combine features of HMO and PPO plans, allowing members to see out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
Importance of Network Coverage
Network coverage is crucial in health insurance plans as it determines which healthcare providers are covered by the insurance policy. In-network providers typically have negotiated rates with the insurance company, resulting in lower out-of-pocket costs for the insured individual.
Tips for Selecting Healthcare Providers
- Check if your preferred providers are in-network to maximize coverage and minimize costs.
- Consider the quality of care provided by healthcare providers, including their credentials, experience, and patient reviews.
- Review the list of covered services and specialties offered by each provider to ensure they meet your healthcare needs.
- Verify the location and accessibility of healthcare providers, considering factors such as proximity to your home or workplace.
Health Policies

Health policies in the context of health insurance refer to the rules, regulations, and guidelines set by insurance companies or governments to determine the coverage and benefits provided by insurance plans.
Influence on Coverage and Benefits
Health policies play a crucial role in shaping the coverage and benefits of insurance plans. They dictate what services are covered, how much will be reimbursed, and under what circumstances. For example, a policy may specify that preventive care services like vaccinations or screenings are fully covered, while elective procedures may require higher out-of-pocket costs.
Impact of Government Regulations
Government regulations heavily influence health insurance policies. These regulations set the standards for what insurance companies can and cannot do, ensuring fair treatment of policyholders and promoting access to essential healthcare services. For instance, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the United States introduced several provisions to protect consumers, such as prohibiting denial of coverage based on pre-existing conditions.
Recent Health Policies
Recent health policies have significantly impacted health insurance coverage. For example, the expansion of Medicaid in certain states under the ACA has extended coverage to low-income individuals. Additionally, the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act requires insurance plans to provide equal coverage for mental health and substance use disorder services, improving access to mental healthcare for many individuals.
Health Records
Health records play a crucial role in the context of health insurance, serving as a comprehensive documentation of an individual’s medical history, treatments, and health status.
Significance of Health Records in Health Insurance
- Health insurance plans may require access to health records to determine coverage eligibility and pre-existing conditions.
- Accurate health records help insurance providers assess the level of risk and set premiums accordingly.
- Health records aid in streamlining the claims process, ensuring prompt reimbursement for medical expenses.
Utilization of Health Records by Insurance Plans
- Insurance plans may use health records to verify the necessity of treatments, prescriptions, or medical procedures.
- Health records assist in coordinating care among different healthcare providers and specialists within the insurance network.
- Insurers may analyze health records to identify trends, patterns, and potential areas for preventive care.
Importance of Maintaining Accurate Health Records
- Keeping health records updated ensures that insurance coverage aligns with the individual’s current health status and needs.
- Accurate health records help prevent claim denials or disputes due to discrepancies or missing information.
- Regularly updating health records enables quick access to essential medical information during emergencies or unforeseen circumstances.
Tips for Organizing and Managing Health Records for Insurance Claims
- Keep all documents in a secure and easily accessible location, such as a dedicated folder or digital storage system.
- Organize records chronologically, including doctor visits, lab results, medications, and insurance correspondence.
- Make copies of important documents and store them both physically and digitally to prevent loss or damage.
- Review and update health records regularly, especially after significant medical events or changes in treatment plans.
Health Screening
Health screening plays a vital role in preventive care by helping individuals detect potential health issues early on, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
Health Insurance Coverage for Health Screenings
Most health insurance plans cover or facilitate various health screenings as part of their preventive care services. These screenings are often included in routine check-ups and are essential for maintaining overall health.
- Annual physical exams: Many health insurance plans cover annual physical exams, which may include blood tests, cholesterol screenings, and other basic health assessments.
- Mammograms: Women’s health insurance plans often cover mammograms for breast cancer screening, typically starting at a certain age or risk level.
- Colonoscopies: Some health insurance plans cover colonoscopies for colorectal cancer screening, usually recommended for individuals over a certain age.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests: Men’s health insurance plans may cover PSA tests for prostate cancer screening, particularly for those at higher risk.
Importance of Regular Health Screenings
Regular health screenings are crucial for maintaining overall health as they can help detect potential health issues early, allowing for prompt treatment and management. By staying up to date with recommended screenings, individuals can take proactive steps in managing their health and reducing the risk of developing serious health conditions.
In conclusion, understanding the various types of health insurance plans equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. Whether you prioritize cost-effectiveness, access to a broad network of providers, or comprehensive benefits, there’s a plan tailored to meet your unique needs.
Questions and Answers
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO?
An HMO typically requires you to choose a primary care physician and get referrals to see specialists, while a PPO allows you to see any healthcare provider without referrals.
How do EPO plans differ from POS plans?
EPO plans require you to use in-network providers for coverage, whereas POS plans offer some coverage for out-of-network care but at a higher cost.
Can I switch between different types of health insurance plans?
It is possible to switch plans during open enrollment periods or if you experience a qualifying life event that allows for a special enrollment period.