
Embark on a journey through the realm of healthcare as we delve into the realm of Interoperability of Health Records in Healthcare. This exploration promises a blend of insights and information that will captivate and educate.
Let’s dive deeper into the intricacies of how interoperability impacts patient care and healthcare efficiency, shedding light on its significance and implications in the modern healthcare landscape.
Interoperability of Health Records in Healthcare
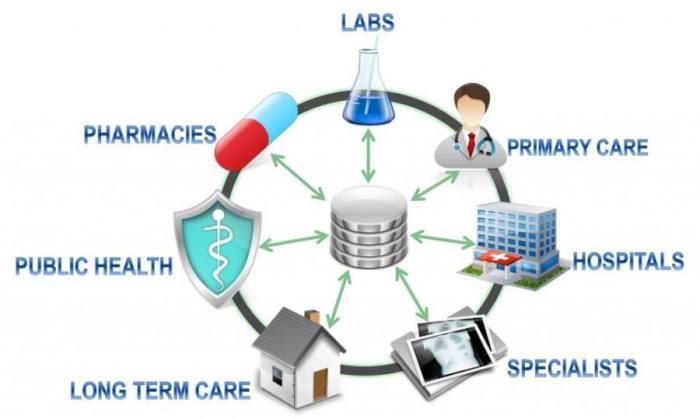
Interoperability in health records refers to the ability of different healthcare information systems and software applications to communicate, exchange data, and use the information that has been exchanged.
Challenges in Achieving Interoperability
One of the major challenges faced in achieving interoperability is the lack of standardized formats for health data. Different systems may use different coding languages or data structures, making it difficult to exchange information seamlessly. Additionally, issues related to data security and privacy pose significant barriers to interoperability.
Importance of Interoperability for Improving Patient Care
- Enhanced Coordination of Care: Interoperability allows healthcare providers to access a patient’s complete medical history, leading to more informed treatment decisions and better coordination of care.
- Reduced Medical Errors: Seamless exchange of health information reduces the likelihood of errors such as duplicate tests or conflicting prescriptions, ultimately improving patient safety.
- Improved Efficiency: Interoperability streamlines processes, reduces administrative burden, and enables faster access to critical health data, leading to more efficient healthcare delivery.
Impact of Interoperability on Healthcare Efficiency
Interoperability plays a crucial role in enhancing healthcare efficiency by eliminating redundant tasks, minimizing delays in care delivery, and facilitating better communication among healthcare providers. This results in cost savings, improved patient outcomes, and overall operational effectiveness within healthcare systems.
Healthcare Access
Interoperability plays a crucial role in enhancing healthcare access by enabling seamless sharing of patient health information across different healthcare providers and systems.
Before and After Interoperable Health Records
Before the implementation of interoperable health records, accessing healthcare services was often hindered by fragmented and incomplete medical records. Patients had to manually gather and transfer their medical information, leading to delays in treatment and potential medical errors. However, after the adoption of interoperable health records, healthcare access has significantly improved. Healthcare providers now have access to comprehensive patient data in real-time, leading to more informed decision-making and coordinated care.
Bridging Gaps for Underserved Populations
Interoperability can bridge gaps in healthcare access for underserved populations by ensuring that all healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care have access to the same up-to-date information. This leads to more personalized and timely interventions, especially for patients who may face barriers to accessing healthcare services due to socioeconomic factors or geographical constraints.
Initiatives Leveraging Interoperability
- Health Information Exchanges (HIEs): HIEs facilitate the exchange of patient health information among healthcare providers within a specific region or community, improving care coordination and access to services.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: Interoperable health records enable remote consultations and monitoring, allowing patients in remote areas or with limited mobility to access healthcare services without the need for in-person visits.
- Patient Portals: Patient portals provide individuals with access to their health records, lab results, and appointment scheduling, empowering patients to take an active role in managing their health and accessing care.
Healthcare Costs
Interoperability of health records in healthcare plays a crucial role in impacting healthcare costs. By allowing seamless sharing of patient information across different healthcare providers and systems, interoperability can lead to significant cost savings.
Reducing Unnecessary Medical Expenses
Interoperability helps reduce unnecessary medical expenses by avoiding duplicate tests, procedures, or treatments. When healthcare providers have access to a patient’s complete medical history through interoperable health records, they can make more informed decisions, leading to better outcomes and cost-effective care.
Cost-Saving Benefits
The cost-saving benefits associated with interoperable health records are evident in various aspects of healthcare delivery. For instance, streamlined communication among healthcare providers can prevent medication errors, reduce hospital readmissions, and improve overall care coordination, ultimately resulting in lower healthcare costs for patients and providers.
Case Studies and Examples
One notable example of cost-effectiveness achieved through interoperability is the Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture (VistA) system used by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. By implementing interoperable health records, the VA has improved care coordination, reduced administrative costs, and enhanced patient outcomes, leading to substantial cost savings over time. Similarly, healthcare organizations that have adopted interoperable health records have seen improvements in efficiency, quality of care, and cost-effectiveness, demonstrating the positive impact of interoperability on healthcare costs.
Healthcare Providers
Interoperability of health records plays a crucial role in the daily operations of healthcare providers, impacting the quality of care they can deliver to patients. By having access to comprehensive and up-to-date patient information across different healthcare settings, providers can make well-informed decisions, improve care coordination, and enhance patient outcomes.
Impact on Healthcare Providers
- Efficient Care Delivery: Interoperable health records enable healthcare providers to access relevant patient data quickly, leading to more efficient diagnosis and treatment.
- Improved Communication: Seamless information exchange fosters better communication among care team members, enhancing collaboration and reducing medical errors.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Providers can engage patients more effectively by sharing health information transparently, promoting shared decision-making, and empowering patients to take an active role in their care.
Challenges in Implementation
- Cost and Resources: Implementing interoperable systems can be costly and resource-intensive for healthcare providers, especially for smaller practices or facilities.
- Technical Compatibility: Ensuring that different systems can communicate effectively with each other poses a technical challenge, requiring interoperability standards and secure data exchange protocols.
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting patient data from breaches and ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA are critical concerns for healthcare providers implementing interoperable health records.
Best Practices for Maximizing Benefits
- Invest in Training: Healthcare providers should invest in training staff on how to effectively use interoperable systems to optimize workflow and ensure data accuracy.
- Standardize Data Entry: Establishing consistent data entry protocols helps maintain data quality and ensures interoperability across different platforms.
- Engage in Continuous Improvement: Regularly assess the performance of interoperable systems, gather feedback from users, and make necessary adjustments to enhance usability and efficiency.
Role in Promoting Interoperability
- Advocate for Standards: Healthcare providers can advocate for the adoption of interoperability standards and policies that facilitate seamless data exchange among healthcare organizations.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Engaging with other healthcare stakeholders, such as EHR vendors, payers, and regulatory bodies, can help drive interoperability initiatives and address common challenges collectively.
- Lead by Example: By demonstrating the benefits of interoperable health records in their practice, healthcare providers can inspire others to embrace interoperability and contribute to a more connected healthcare ecosystem.
Health Insurance
Interoperability plays a crucial role in the operations of health insurance companies, streamlining processes related to claims processing, coverage, and reimbursement.
Role of Interoperability in Health Insurance Operations
Interoperable health records allow health insurance companies to access comprehensive patient information from various healthcare providers seamlessly. This enables insurers to make more informed decisions regarding coverage, claims processing, and reimbursement.
Streamlining Insurance Claims Processing
- Interoperable health records reduce administrative burden by providing insurers with real-time access to accurate patient data, resulting in faster claims processing.
- Automation of data exchange between healthcare providers and insurers through interoperable systems minimizes errors and delays in claim submissions and approvals.
- Efficient claims processing improves the overall patient experience by ensuring timely reimbursement for healthcare services.
Impact on Insurance Coverage and Reimbursement Processes
- Enhanced interoperability leads to better coordination between healthcare providers and insurers, improving the accuracy of coverage determinations and reimbursement decisions.
- Real-time access to patient data allows insurers to tailor coverage plans based on individual health needs, promoting proactive and preventive care.
- Streamlined reimbursement processes result in faster payments to healthcare providers, fostering better relationships between insurers and the healthcare community.
Collaborations Between Health Insurers and Healthcare Providers
- Health insurers and healthcare providers are increasingly collaborating to implement interoperable systems that facilitate seamless data sharing and improve patient outcomes.
- Joint initiatives focus on standardizing data formats, enhancing data security measures, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements to promote interoperability.
- Examples of successful collaborations include the development of shared electronic health record platforms and interoperable telehealth solutions to enhance care delivery and optimize insurance processes.
Health Policies
Health policies play a crucial role in shaping the interoperability of health records within the healthcare system. These policies provide guidelines and regulations that govern how health data is shared and accessed among different healthcare entities.
Influence of Health Policies on Interoperability
Health policies influence the interoperability of health records by setting standards and requirements for data exchange. These policies ensure that healthcare providers, payers, and other stakeholders adhere to specific protocols when sharing patient information.
Current Regulatory Frameworks
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States sets standards for the protection of sensitive patient data and mandates secure electronic transactions.
- The 21st Century Cures Act promotes interoperability and prohibits information blocking, encouraging seamless exchange of health information.
- The European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) governs the processing of personal data, including health information, within the European Union.
Role of Government Policies
Government policies play a key role in promoting interoperability standards by incentivizing healthcare organizations to adopt interoperable systems and technologies. These policies encourage the development and implementation of interoperable health IT solutions to improve care coordination and patient outcomes.
Future of Health Policies
Looking ahead, the future of health policies in advancing interoperable health records is focused on enhancing data exchange capabilities, addressing privacy concerns, and fostering innovation in healthcare technology. As technology continues to evolve, policymakers will need to adapt regulations to ensure seamless interoperability while safeguarding patient data.
Health Records
Standardized health records play a crucial role in ensuring interoperability within healthcare systems. By having a uniform format for storing and sharing patient information, healthcare providers can easily access and exchange data, leading to improved care coordination and patient outcomes.
Significance of Standardized Health Records
- Standardized health records facilitate seamless communication between different healthcare facilities, ensuring that all providers have access to the same information about a patient.
- They help reduce errors in data entry and interpretation, leading to more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Standardization also enables the use of health information exchange (HIE) systems, allowing for secure sharing of patient data across different organizations.
Challenges in Data Privacy and Security
- One of the main challenges in interoperable health records is maintaining data privacy and security. With sensitive information being shared across multiple platforms, the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access increases.
- Ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is essential to protect patient confidentiality and prevent data misuse.
- Implementing robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, is crucial to safeguard patient information in a unified health record system.
Benefits of a Unified Health Record System
- A unified health record system allows for a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, regardless of where they receive care. This leads to more informed decision-making and personalized treatment plans.
- Improved care coordination and communication among healthcare providers result in better patient outcomes and reduced duplicative tests or procedures.
- Patient engagement is enhanced when individuals can easily access and share their health records with different providers, empowering them to take an active role in their healthcare.
Technologies for Secure Health Record Sharing
- Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to store and share health records, ensuring data integrity and reducing the risk of tampering or unauthorized access.
- Health information exchange (HIE) platforms provide a centralized system for exchanging patient information among healthcare organizations while maintaining strict security protocols.
- Data encryption and tokenization techniques help protect sensitive health data during transmission and storage, safeguarding patient privacy in interoperable systems.
Health Screening

Interoperable health records play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of health screening processes within the healthcare system. By enabling seamless sharing of patient information among different healthcare providers, interoperability streamlines the screening procedures and ensures that all relevant data is easily accessible.
Facilitation of Health Screening Processes
Interoperable health records allow healthcare professionals to access a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, test results, and previous screenings from various sources. This comprehensive data sharing enables a more accurate assessment of the individual’s health status and risk factors, leading to more personalized and effective screening recommendations.
- Interoperability eliminates the need for redundant tests and screenings, reducing unnecessary costs and minimizing the risk of duplicate procedures.
- Health screenings can be conducted more efficiently and proactively, enabling early detection of potential health issues and timely interventions.
- Patients benefit from a more coordinated and integrated approach to healthcare, ensuring that screening results are readily available to all involved healthcare providers.
Improving Accuracy and Efficiency
Interoperable health records enhance the accuracy and efficiency of health screenings by providing real-time access to up-to-date patient information, including recent test results, medications, and treatment plans. This accessibility enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions and recommendations based on the most current data available.
“Interoperability streamlines the screening procedures and ensures that all relevant data is easily accessible.”
- Health screenings can be tailored to each individual’s specific health needs and risk factors, leading to more targeted interventions and preventive measures.
- Interoperability reduces the likelihood of errors or omissions in screening processes, promoting a higher standard of care and patient safety.
- Healthcare providers can collaborate more effectively in the screening process, sharing insights and best practices to improve overall healthcare outcomes.
Impact on Preventive Healthcare Measures
Interoperable health records have a significant impact on preventive healthcare measures by enabling proactive and personalized screening programs that focus on early detection and prevention. Through data-driven insights and predictive analytics, healthcare providers can identify individuals at higher risk of developing certain conditions and implement targeted screening strategies to mitigate these risks.
- Interoperability supports population health management initiatives by tracking and monitoring health trends and outcomes across diverse patient populations.
- Health screening programs can be more effectively coordinated and monitored, ensuring that individuals receive timely screenings based on their unique health profiles.
- Interoperable health records empower patients to take an active role in their own health by providing access to their screening results and encouraging preventive healthcare behaviors.
Innovative Health Screening Programs
Interoperability has paved the way for innovative health screening programs that leverage technology and data analytics to enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of screenings. Examples include remote monitoring solutions, mobile health apps for self-assessment, and telemedicine platforms that enable virtual screenings and consultations.
- Telemedicine platforms allow patients to undergo health screenings remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits and expanding access to care in underserved areas.
- Mobile health apps provide individuals with tools to track their health metrics, receive personalized screening recommendations, and access educational resources on preventive healthcare.
- Remote monitoring solutions enable continuous monitoring of vital signs and health parameters, alerting healthcare providers to any abnormal changes that may require immediate attention or follow-up screenings.
In conclusion, the discussion on Interoperability of Health Records in Healthcare illuminates the critical role it plays in revolutionizing patient care delivery and streamlining healthcare processes. As we look towards the future, embracing interoperability will undoubtedly pave the way for enhanced healthcare outcomes and experiences for all stakeholders involved.
Essential Questionnaire
How does interoperability benefit patient care?
Interoperability ensures that health records are seamlessly shared among healthcare providers, leading to better coordination of care and improved treatment outcomes for patients.
What are some challenges in achieving interoperability in healthcare?
Challenges include varying data standards, incompatible systems, and concerns regarding data security and privacy.
How can healthcare providers maximize the benefits of interoperable health records?
Healthcare providers can optimize interoperability by investing in training, adopting user-friendly systems, and actively engaging in data sharing initiatives.





